-
Categories
The 5G TALKS: Episode 9 - Meet our Korean Trial Site

Our next interview is with our Korean Trial Site leader, Korea Automotive Technology Institute. One of 5G-MOBIX consortium partners, KATECH is active in several areas in the Korean Automotive Industry such as smart and autonomous vehicles, AI mobility, green vehicles, advanced materials, reliability and hydrogen mobility. As a non-profit research institute funded by the Korean government, not only does KATECH support central and local governments’ automotive R&D policy, but also plans large-scale national government projects and takes on the responsibility of automotive parts assessment and certification. The Institute leads the 5G-MOBIX Korean Trial Site and works closely with different technical background partners such as ETRI, SNETICT, and Renault Samsung Motors to carry out two CCAM use cases, namely tethering and remote controlling a vehicle via mmWAVE communication.
What role does the 5G-MOBIX project play in KATECH’s own strategy and what motivated you to join the consortium?
The project’s main objectives are developing, testing, and validating innovative cooperative connected and automated mobility (CCAM) functionalities based on 5G core technology along cross-border corridors and this precisely matches KATECH’s own objectives to promote and encourage innovation of cooperative automated vehicle technology and to harmonize all the stakeholders’ strategical technologies related to 5G. As the Korean Trial Site leader, KATECH provides key findings of remote-controlled vehicle use cases based on Level 4 Automated Vehicles. In addition, being the Coordinator of the Korean Trial Site, KATECH takes charge of the overall project activities in South Korea. Within the framework of 5G-MOBIX, apart from having the goal of improving automated vehicles based on 5G technology, KATECH also expects to share key findings concerning the results of the CCAM use cases on different 5G frequencies between Korea and EU partners.
Tell us more about the 5G-MOBIX Korean Trial Site. What makes it unique for the testing of 5G?
The Korean Trial Site makes use of two testing sites, namely KATECH’s testing grounds and Yeoju Highway testing site. KATECH’s own testing ground is used to test remote-controlled vehicle use case and it offers two types of closed test roads; a 1 km patch of different types of test roads (i.e. Belgian pavé road, straight lane, braking track) and a test road mimicking an urban setting with multiple intersections and a roundabout.
The Yeoju Highway test track is located between Yeoju junction (JCT) and Gamgok interchange (IC) of Highway 45 of Korea, which was built parallel to the main highway. Out of total 7.7 km test track, a section of 2.7 km is actually used for the trial, where 5 DUs are deployed along the test track as illustrated in the figure below. The DUs are marked from ``1'' to ``5'' and the starting position of the vehicle is marked ``S''. The distance between the consecutive DUs is from 450 m to 750m. Each DU is mounted on a road side steel pole 15 m above the ground. Two cores of optical fibers are connected to each DU: One for the fronthaul connection to the CU and the other for the synchronized operation among the DUs.
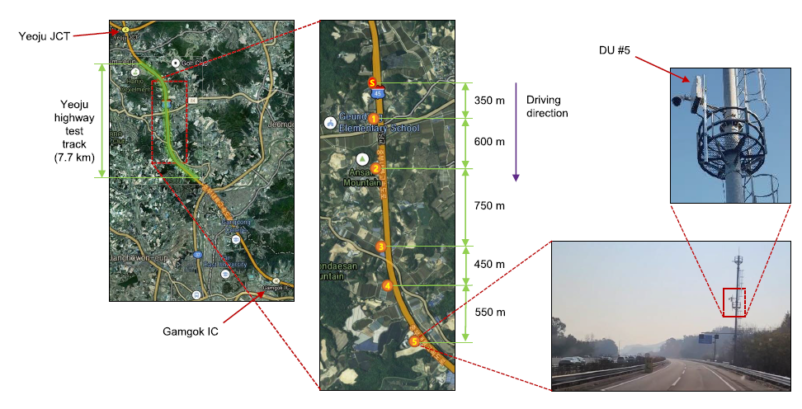 Figure 1 - DU(RSU) deployment on a Yeoju highway test track
Figure 1 - DU(RSU) deployment on a Yeoju highway test track
In the Korean Trial Site, ETRI and SNETICT provide mmWAVE (SA) network (base station and 5G Core network) while KATECH provides the remote-controlled vehicle, a Renault Arkana based on mmWAVE with the technical support of Renault Samsung Motors. Korean partners developed the mmWAVE (SA) network based on 5G NR release 15 standards. The 5G core network, developed by SNETICT, is comprised of protocol stacks such as UPF, AMF and SMF. Other components, developed by ETRI, are gNB and the terminal equipment, which are integrated into the remote-controlled vehicle. Furthermore, the mmWAVE network that the Korean partners developed is fully integrated into the vehicle as well.
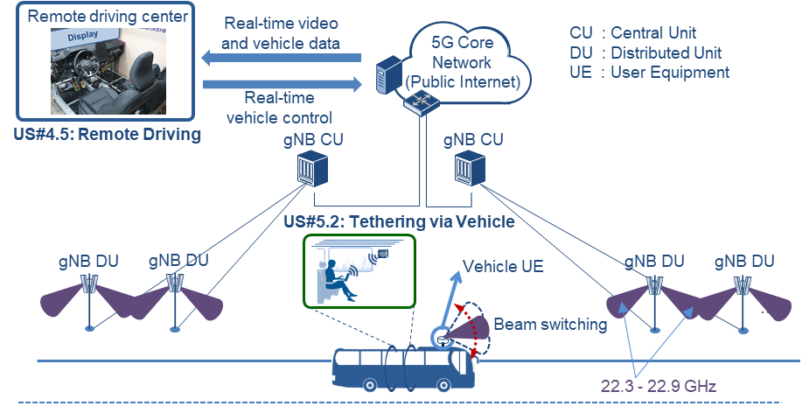 Figure 2 - User stories and network architecture
Figure 2 - User stories and network architecture
Can you give us any updates on the latest trials done on the Korean Trial Site? Which are some of the latest developments?
There are two use cases in the Korean trial site: remote-controlled vehicle and tethering via mmWAVE communication. KATECH is currently carrying out the first use case “remote-controlled vehicle via mmWAVE communication”. A Level 4 automated vehicle, in this case a Renault Arkana, is equipped with a mmWAVE OBU and is used to test and validate remote-control use cases. There are a total of 8 cameras (front, left, right, rear, and 4 cameras for surround-view monitoring) equipped for real-time video streaming to the remote server through mmWAVE communication found in the test vehicle. A remote control station was developed using real automotive parts from a Renault Arkana. The mmWAVE base station and core network are mounted in the moving base station vehicle, a Renault Master van with a remote control station. During the field trial, the key functionalities (real-time video streaming and control RCV via mmWAVE communication) are tested and validated.
 Figure 3 - Field trial of the remote controlled vehicle use case via mmWAVE communication in KATECH testing ground - South Korea
Figure 3 - Field trial of the remote controlled vehicle use case via mmWAVE communication in KATECH testing ground - South Korea
On the other hand, ETRI have been conducting a field trial of the tethering use case on a highway test track in Yeoju, Korea. The field trial was conducted using a mmWave OBU (vehicle UE) which was installed on the test vehicle and network equipment including 5G core and five gNB DUs deployed along the trackside. During the field trial, the key functionalities (i.e. beam switching and handover) have been successfully tested and validated.
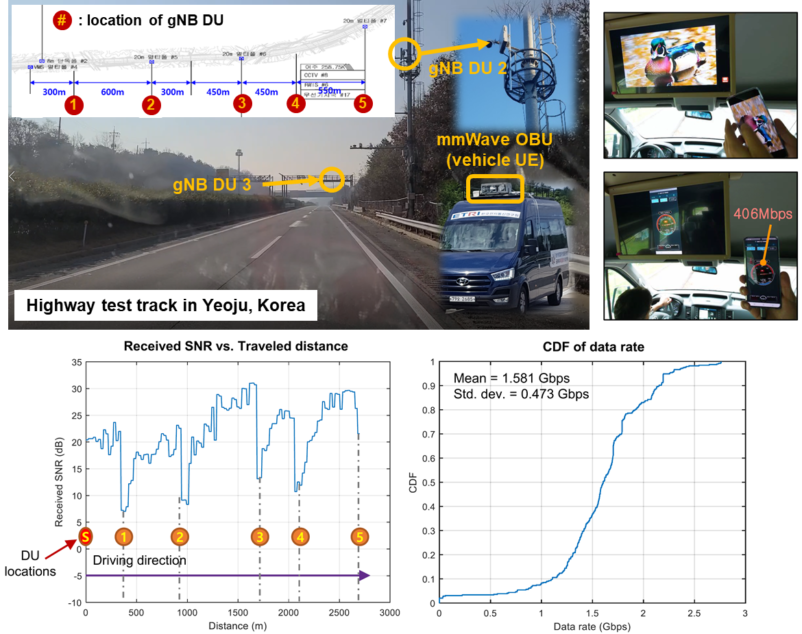 Figure 4 - Field trial of the tethering via mmWAVE communication use case conducted on a highway test track in Yeoju, Korea.
Figure 4 - Field trial of the tethering via mmWAVE communication use case conducted on a highway test track in Yeoju, Korea.
What are your next steps in the project?
We have successfully developed, tested, and validated mmWAVE network system and integrated it into the remote control vehicle. We are now preparing to test the remote-controlled vehicle via mmWAVE communication link at KATECH’s closed testing ground with predefined scenarios such as high-speed maneuvering with the remote-controlled vehicle, and various other maneuvers such as lane changing and avoiding a sudden obstacle.

To find out more about the Korean Trial Site, click here.